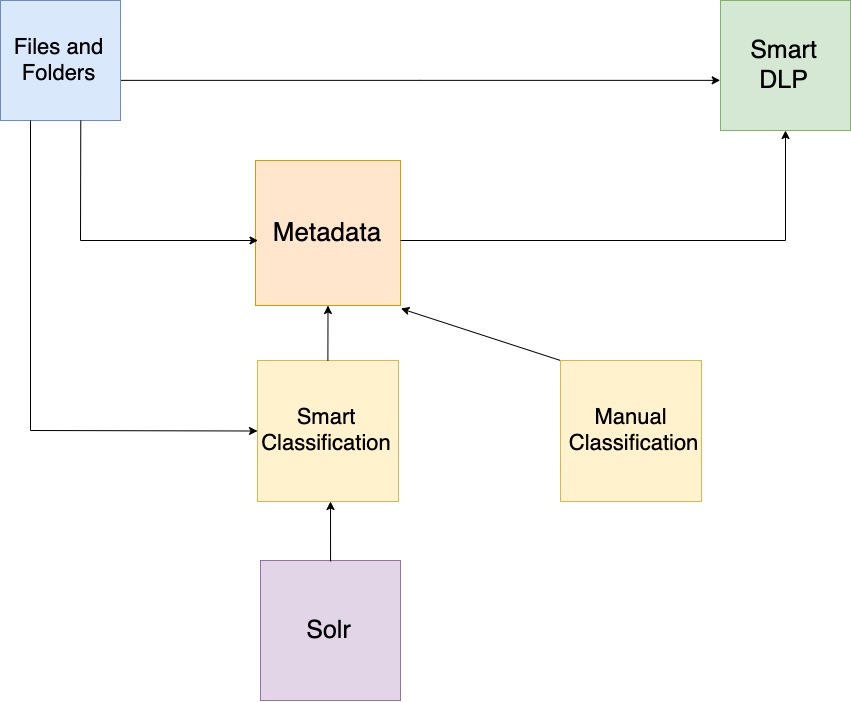
Metadata, Smart Classification, and Smart DLP
Metadata, Smart Classification, and Smart DLP are all part of FileCloud’s advanced security technology. However, there are distinct differences between these features that affect how they are used and how they interact with one another.
Metadata
Metadata – information about files and folders – identifies what the file or folder contains and how much protection it should receive.
Examples of metadata include:
Phone numbers
Credit card numbers
PII security priority
EXIF image data
Upload date
Boolean values
Metadata can be created, edited, and applied with no dependencies.
Learn more about metadata.
Smart Classification
The Smart Content Classification Engine (CCE) further refines how files are organized and tracked by FileCloud. With one or more sets of initial metadata, classification can automatically add or alter metadata. Examples of smart content classification rules include:
For files containing nine-digit credit card numbers, mark PII security level as “HIGH"
For images larger than 15MB, add the text attribute “PRINT PROOFS"
For PDFs with the metadata text attribute “Holiday vacation requests” uploaded after October 1st, add the text attribute “HOLIDAY REQUESTS” and the number attribute “2019”.
Smart Classification relies on metadata in order to operate. A minimum of one set of metadata is required to run CCE; using more than one smart classification rule allows for a greater degree of classification.
Learn more about Smart Classification.
CCE scans every file and folder on the FileCloud installation. However, the parameters of the CCE rule determine which files undergo classification.
Smart DLP
Smart Data Leak Prevention (DLP) applies user-created rules in order to strictly control who can access the FileCloud installation, in addition to restricting which files and folders they can download or share. DLP rules can control access based on many different parameters, including user name, IP address, file path, and applied metadata. Smart DLP can also return information about who is attempting to access the FileCloud installation. Examples of DLP include:
Deny users of the group “accounting” from downloading or sharing files.
Allow users with emails from the domain “example.com” to login to the FileCloud installation and share files but deny users the ability to download files.
Deny downloads of files with metadata attribute “GDPR” set to “YES".
Return the usernames, IP addresses, user agents, and file paths for everyone accessing the FileCloud installation.
DLP can operate with or without metadata or prior classification.
Learn more about Smart DLP.