Configure Storage for HA
The storage setup covered here is intended to help you set up your HA environment, but is outside the scope of FileCloud Support.
We use SAMBA Share on RHEL in our example, but you may use the file sharing software that best serves your needs.
In a Windows environment, the Apache service should be able to read and write to the storage path; this typically requires modifying the Apache service log-on permissions to run as a user account with full privileges to the storage path.
The storage path created to store FileCloud data should be accessible across all the web nodes in the setup and readable/writable for Apache.
To install Samba in RHEL, run:
yum update -y yum install samba -y
Then, enable and check Samba status:
systemctl enable --now smb systemctl status smb
Now that Samba is installed, create a directory for it to share.
The command below creates a new folder /data/filecloud and sets proper Samba permissions by an authenticated user who should have full permissions to the share.mkdir -p /data/filecloud adduser --home /data/filecloud --no-create-home --shell /usr/sbin/nologin --group sambashare filecloud chmod 2770 /data/filecloud chown filecloud:sambashare /data/filecloud
Samba keeps its own database of users and passwords, which it uses to authenticate logins. In order to log in, all users must be added to the Samba server and enabled.
Execute the followingsmbpasswdcommands to accomplish both of these tasks:smbpasswd -a filecloud smbpasswd -e filecloud
The configuration file for Samba is located at
/etc/samba/smb.conf. To add the new directory as a share, edit the file by running:vi /etc/samba/smb.conf
Below is the samba conf sample used in this setup:
[global] server string = samba_server server role = standalone server interfaces = 192.0.2.0 bind interfaces only = yes disable netbios = yes smb ports = 445 log file = /var/log/samba/smb.log max log size = 10000 [filecloud] path = /data/filecloud browseable = yes read only = no force create mode = 0660 force directory mode = 2770 valid users = filecloud
To mount the Samba share in your FileCloud web server nodes, see How to properly mount a CIFS share on RHEL for FileCloud.
Set up the managed storage path in FileCloud
Since the FileCloud app server nodes do not store any of the application data, managed storage must reside in an external location (NAS, ISCSI, SAN, Amazon S3, or OpenStack)
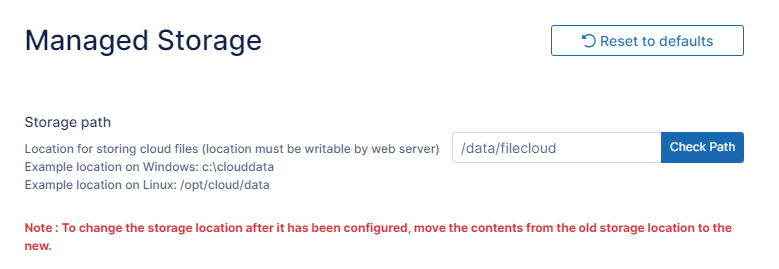
In this example, the storage path is /data/filecloud which is already available and mounted on each of the Linux webserver nodes.
- Open the FileCloud Admin portal at http://<load balancer IP>/ui/admin/index.html or http://<Private IP of Web Server>/ui/admin/index.html and log in.
- In the FileCloud admin portal's left navigation bar, scroll down and click Settings. Then, on the Settings navigation page, click Storage .
The Managed Storage settings page opens by default. - Enter the mounted path in Storage Path, and click Save.
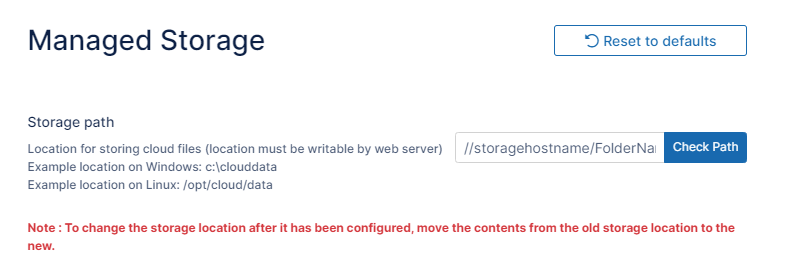
In Windows, the path must be a UNC path that is accessible from all web nodes. Here the example path is //storagehostname/FolderName.
To enable encryption for FileCloud managed storage, see Enabling Storage Encryption.
If you are using S3 object storage see Setting up FileCloud Managed S3 Storage.
If you are using Azure blob storage, see Setting up FileCloud Managed Azure Blob Storage.