
This post was originally published on April 15, 2021 and updated to discuss CMMC 2.0 changes on April 13, 2022.
What is CMMC?
CMMC is a certification standard used by the US Government to audit third-party compliance with NIST SP 800-171. DoD third-party organizations have been required to comply with NIST 800-171 since January 1, 2018. However, the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) has struggled with a low rate of NIST 800-171 compliance across the Defense Industrial Base.
CMMC was created in January 2020 to address that systemic issue of non-compliance by both primaries and their subs. Furthermore, CMMC was intended to fill a gap in 3rd-party auditing capabilities to support NIST 800-171 compliance requirements, which was not available prior.
The first iteration of CMMC (also referred to as CMMC 1.0) was designed with an "assessments framework" in mind. This framework was modeled on five levels of maturity, which are covered in detail below. This is the current operating level of CMMC compliance. CMMC 2.0 has been developed in response to an internal review following public commentary regarding the September 2020 “CMMC 1.0” interim rule.
Following the internal review, the DoD published an Advance Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (ANPRM) on November 17, 2021. The proposed changes comprise CMMC 2.0 and will take effect after the rulemaking process is completed (anywhere from 9 to 24 months from November 2021.) For more information on CMMC 2.0 requirements, check out our blog post.
However, since CMMC 1.0 is still in effect as an interim rule, here is everything you need to know about the requirements and how FileCloud can help meet them. (You can also download our CMMC white paper here.)
Why is CMMC important?
The Center for Strategic and International Studies estimates that the total global cost of cybercrime was is approaching $1 trillion, as of the survey conducted in 2020. The DoD is enforcing a risk-management approach to improve cybersecurity measures of third-party partners by asking them to obtain the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC). This certification is designed to improve the protection of Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and Federal Contract information (FCI), and the certification applies to DoD contractors.
CMMC measures an organization’s approach to protect FCI and CUI. CUI is information that requires protection or audit controls according to federal law, regulations, and government policies. FCI is information provided by or generated by the government under a contract to develop or deliver a product or service to the government, not intended for public release.
Key Takeaways for CMMC
- All companies conducting business with the DoD, including subcontractors, must be certified.
- The CMMC is expected to combine relevant portions of various cybersecurity standards, such as NIST SP 800-171, NIST SP 800-53, ISO 270001, and ISO 27032, into one unified standard for cybersecurity.
- Contractors will be required to be certified by a third-party auditor.
- Certification levels of contractors will be made public, though details of specific findings will not be publicly accessible.
- Contractors must clearly document practices and procedures with those requirements that already comply with CMMC practices or processes.
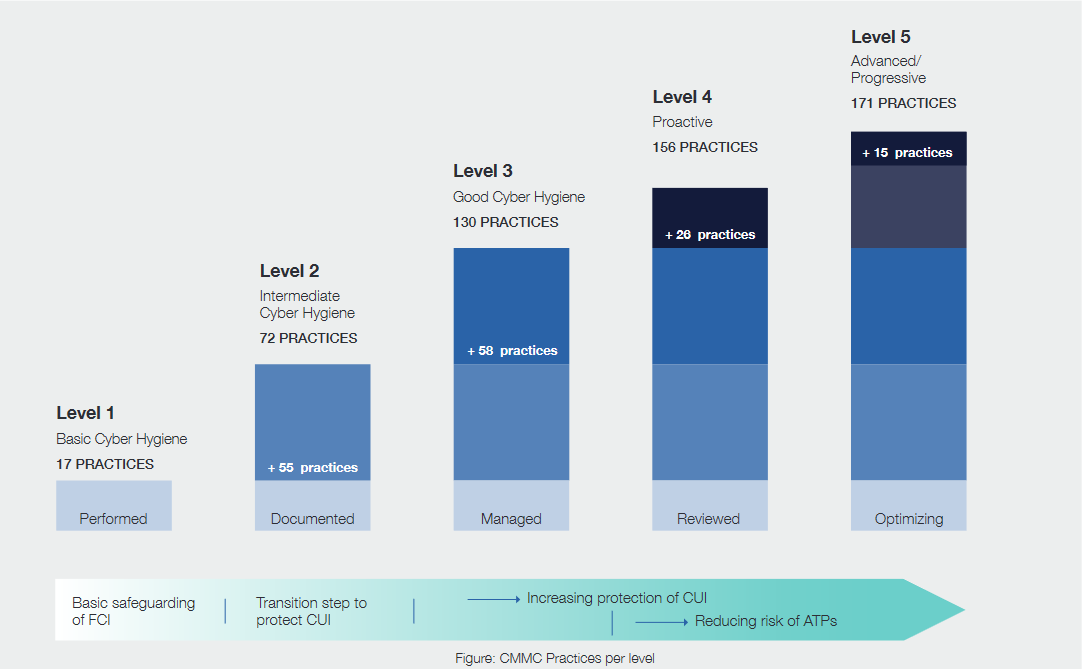
Five Levels of Maturity
Depending on your company and the business you conduct with the DoD will decide which level (1–5) you need.
- Level 1 – Basic Cyber Hygiene: Includes basic cybersecurity suitable for small companies having a subset of universally accepted common practices. The processes at this level would include some basic performed cybersecurity practices. This level has 35 security controls that must be implemented successfully.
- Level 2 – Intermediate Cyber Hygiene: Includes universally accepted cybersecurity best practices. Practices at this level should be documented, and access to CUI will require multi-factor authentication. This level includes an additional 115 security controls on top of Level 1.
- Level 3 – Good Cyber Hygiene: Includes coverage of all NIST SP 800-171 Rev. 1 controls and additional practices beyond the scope of current CUI protection. Processes at this level are maintained, and there is a comprehensive knowledge of cyber assets. This level requires an additional 91 security controls on top of those covered in Levels 1 and 2.
- Level 4 – Proactive: Includes advanced and sophisticated cybersecurity practices. The processes at this level are periodically reviewed, properly resourced, and are improved regularly across the enterprise. In addition, the defensive responses operate at high speed and there is a knowledge of all cyber assets. This level has an additional 95 controls on top of the first three Levels.
- Level 5 – Advanced / Progressive: Includes highly advanced cybersecurity practices. The processes involved at this level include continuous improvement across the enterprise and defensive responses performed at high speed. This level requires an additional 34 controls.
17 Domains of Security Requirements
The CMMC model consists of 17 domains, 14 of which are derived from the Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) Publication 200 and NIST 800-171
- Access Control
- Asset Management
- Audit and Accountability
- Awareness and Training
- Configuration Management
- Identification and Authentication
- Incident Response
- Maintenance
- Media Protection
- Personnel Security
- Physical Protection
- Recovery
- Risk Management
- Security Assessment
- Situational Awareness
- System and Communication Protection
- System and Information Integrity
FileCloud identifies loopholes in critical security controls according to your desired CMMC maturity level for each of the 17 domains and creates clear instructions for both improving your security position and meeting CMMC requirements. We will go through several domains and let you know how FileCloud helps you comply.
Access Control - FileCloud supports integration with Active Directory, LDAP, and SSO. In addition, FileCloud integrates your Network Shares with NTFS permissions to provide you with better access control of the data your users are allowed to view, upload, download, share, sync, or manage. Within FileCloud you can create users and groups and assign permissions and policies to them to allow or prevent them from accessing your data. FileCloud also supports DLP and granular folder permissions.
Asset Management - FileCloud’s Centralized Device Management allows you to view all the devices that have access to FileCloud using our mobile and desktop clients. FileCloud also includes functionality for creating reports of these devices to aid you in creating your inventory report.
Audit and Accountability -FileCloud’s auditing capabilities enable you to review who, when, where, and what is involved each time FileCloud is accessed. FileCloud also supports SIEM (blah) integration. FileCloud’s data governance capabilities allow you to apply multiple retention rules to avoid the deletion of auditable records you want to store in FileCloud.
Awareness and Training -To complement your internal employee training, FileCloud provides you with extensive information about applying best security practices while using FileCloud. FileCloud also offers end–user training.
Configuration Management- FileCloud contains multiple configuration capabilities including but not limited to centralized device management, content classification, DLP, global policies, specific device configuration policies, Customization, Data Governance, user password enforcement, private sharing permissions, granular folder level permissions, etc.
Identification and Authentication-Besides FileCloud’s proprietary user authentication, FileCloud supports integration with Active Directory, LDAP, and SSO. FileCloud also supports Duo Security integration and 2FA.
Incident Response-FileCloud’s data governance dashboard displays potential rule violations such as DLP violations or retention policy violations. FileCloud workflows enable you to automate report generation, device approval, and other tasks.
Maintenance- Using FileCloud workflows, administrators have the ability to perform automatic maintenance tasks within FileCloud, for example, deleting files after a specified amount of time or disabling users who have not accessed FileCloud in a specific amount of time. FileCloud also supports automatic audit log trimming and exporting to a location defined by the administrator.
Media Protection-FileCloud’s antivirus integration via ClamAV or ICAP protocol enables you to verify the integrity of files as they are uploaded. FileCloud’s DLP provides you with granular control over your data. FileCloud supports in–transit encryption via HTTPS/SSL.
Personnel Security-FileCloud’s smart classification and DLP enable you to classify your data based on DLP rules that deny or allow downloads or sharing.
Recovery- The FileCloud Server Backup tool creates backs up your data automatically.
Conclusion
For your organizations to be CMMC Compliant, they must implement encrypted file sharing solutions. The end-user is responsible for utilizing suitable FileCloud capabilities as well as managing and maintaining the environment where FileCloud is being hosted to ensure the CMMC requirements are being met.
FileCloud is the commercial of the shelf software solution that helps businesses securely share, manage, and govern enterprise content. FileCloud software provides the necessary capabilities for organizations to obtain CMMC compliance.
References
Accellion CMMC Compliance Guide. (n.d.). ACCELLION. Retrieved 2021, from https://www.accellion.com/sites/default/files/resources/wp-accellion-cmmc-compliance-guide.pdf
Carey, B. (2020, May 11). Prepare for CYBERSECURITY Maturity Model certification (cmmc). Retrieved April 06, 2021, from https://blog.rapid7.com/2020/04/15/preparing-for-the-cybersecurity-maturity-model-certification-cmmc-part-1-practice-and-process/
Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) & www.mcafee.com. (2018, February). Economic Impact of Cybercrime— No Slowing Down. Retrieved April 6, 2021, from https://csis-website-prod.s3.amazonaws.com/s3fs-public/publication/economic-impact-cybercrime.pdf
Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) (Vol. 1). (2020). Carnegie Mellon University and The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory LLC.
DoD Cybersecurity Audits are Coming: Here's how to prepare. (2021). Retrieved April 06, 2021, from https://www.sysarc.com/services/managed-security-services/cybersecurity-maturity-model-certification-cmmc-guide-for-dod-contractors/

By Team FileCloud