Competitor Series: FileCloud vs Dropbox
This comprehensive comparison is the next in our competitor series. In this post, we measure FileCloud Enterprise Essentials against Dropbox Advanced to help you understand why FileCloud might be the better choice for your enterprise needs.
A Dropbox Alternative: Why IT Leaders Choose FileCloud Online for Enterprise File Sharing
The shift from consumer-grade file sharing to enterprise-focused solutions has accelerated dramatically over the past decade. While Dropbox built its reputation on simplicity and ease of use, FileCloud was designed from the ground up with enterprise requirements in mind. This fundamental difference in approach becomes apparent when evaluating critical features across data control and governance.
FileCloud serves as a comprehensive EFSS Dropbox alternative that doesn't require you to sacrifice functionality for security. Dropbox is built on public cloud infrastructure; FileCloud recognizes that different industries and organizations have varying needs for data control, compliance, and integration capabilities that public cloud services might not be able to meet.
This flexibility has made FileCloud particularly attractive to organizations in healthcare, finance, government, and other highly regulated sectors where data sovereignty isn't just preferred—it's mandatory. Features such as data residency, compliance support, workflow automation, and large file sharing aren't afterthoughts or premium add-ons. They're core components of the FileCloud experience, making it easier for IT teams to maintain security standards while enabling productivity across the organization.

Dropbox vs FileCloud: Deployment
One of the most significant differentiators in the FileCloud vs Dropbox comparison lies in deployment flexibility. Dropbox operates exclusively as a cloud-based SaaS solution, which means enterprise data uploaded to Dropbox resides on their servers, with limited options for customization or control over the infrastructure.
FileCloud takes a dramatically different approach by offering multiple deployment options. Organizations can choose from cloud hosting, on-premises deployment, or hybrid configurations that combine both approaches. This flexibility is crucial for organizations with specific data residency requirements, existing infrastructure investments, or security policies that mandate on-site data storage.
For IT leaders dealing with regulatory requirements or organizational policies that restrict cloud storage, FileCloud's on-premises option provides a complete file sharing and collaboration solution without requiring data to leave your network perimeter. The hybrid model offers an ideal middle ground, allowing organizations to keep sensitive data on-premises while leveraging cloud capabilities for less critical content and remote access scenarios.
For enterprises that require high availability, disaster recovery, and scalability, FileCloud ServerLink is a powerful tool for branch replication. Each site runs its own instance of FileCloud, but data is synced across each, so all sites have the most up-to-date versions of files, and if one instance goes down, whether due to a natural disaster, cyberattack, or infrastructure malfunction, the others remain stable, preserving critical business data.

FileCloud’s deployment flexibility also extends to integration capabilities. FileCloud can seamlessly integrate with existing Active Directory implementations, LDAP systems, and other enterprise infrastructure components that many organizations rely on for user management and authentication.
Dropbox vs FileCloud: Admin Capabilities
Administrative control represents another area where FileCloud vs Dropbox reveals significant differences in enterprise readiness. Dropbox's admin panel is user-friendly, but it offers relatively basic controls across users and groups, activity, settings, security, and billing. Admins responsible for complex integrated infrastructure, in which data is highly regulated, may benefit from more granular management capabilities.
FileCloud provides comprehensive administrative features that give IT teams the level of control they need to manage enterprise deployments effectively. Administrators can set detailed user permissions, create custom roles, manage device access, and implement sophisticated retention, classification, and data loss prevention policies.
The platform includes advanced user provisioning capabilities, bulk user management tools, and detailed reporting features that help administrators understand how the system is being used across the organization. The comprehensive audit logs capture all activity within the system, and these logs can easily be exported for internal review or external regulatory cycles.

Dropbox vs FileCloud: Security
Security represents perhaps the most critical differentiator for enterprise buyers evaluating EFSS solutions. While Dropbox provides reasonable security for general business use, FileCloud's security architecture was designed to meet demanding enterprise requirements.
FileCloud implements multiple layers of security, including end-to-end encryption, advanced threat protection, and Zero Trust sharing capabilities that ensure even FileCloud administrators cannot access encrypted data. The platform supports advanced authentication methods, including multi-factor authentication, SAML-based single sign-on, and integration with enterprise identity management systems.
For organizations with heightened security requirements, FileCloud's on-premises deployment option ensures that sensitive data never leaves the organization's control, while still providing modern file sharing and collaboration capabilities that users expect.

Dropbox vs FileCloud: Compliance & Governance
Regulatory compliance and data governance represent areas where many organizations find Dropbox's capabilities insufficient for their needs. FileCloud was built with compliance requirements in mind, offering a built-in compliance dashboard to help organizations meet HIPAA, GDPR, ITAR, NIST, and PDPL requirements.
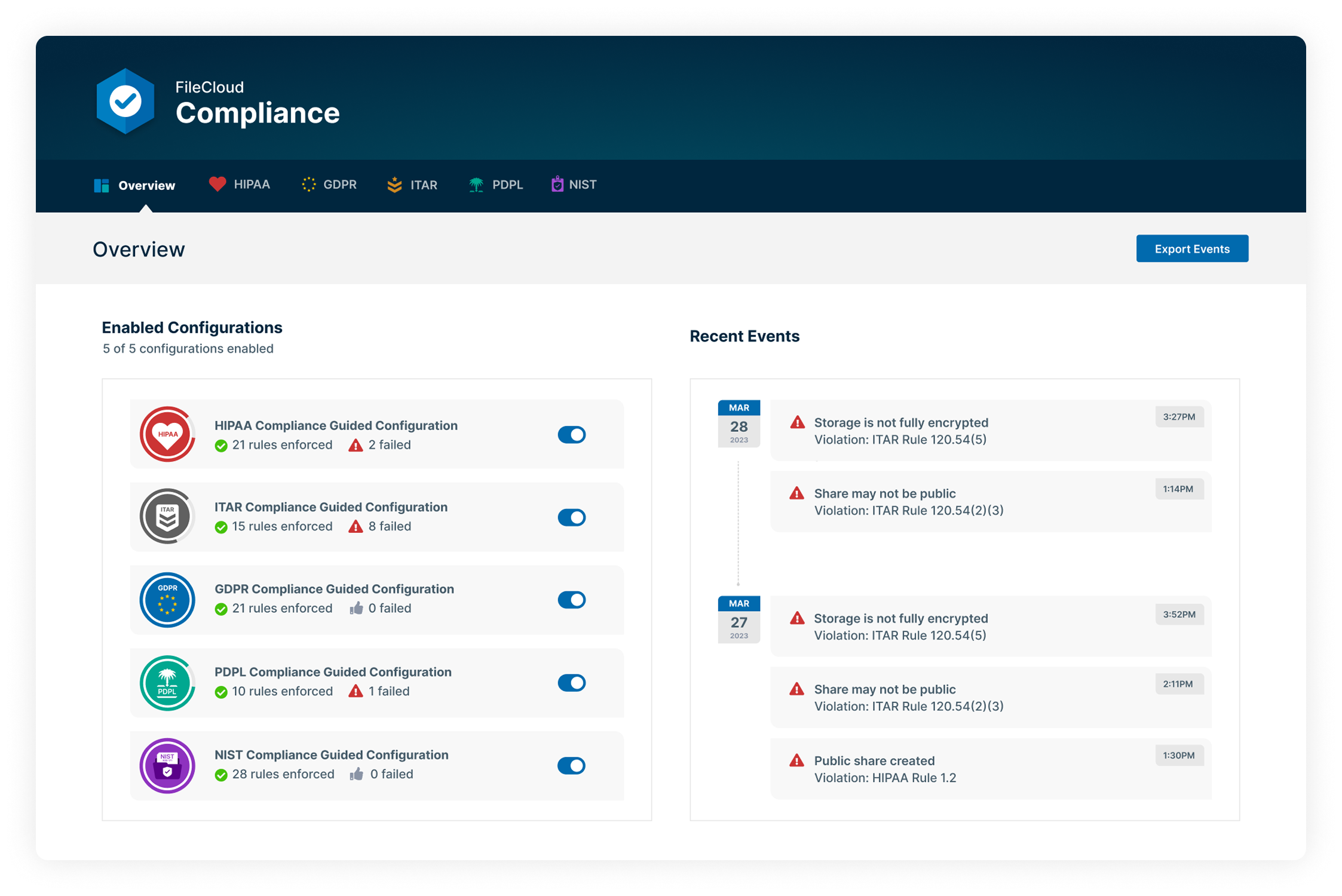
FileCloud also offers compliance support for other regulations such as CMMC, EU DORA, SEC Rule 17a-4(f), FDA 21 CFR 11, Sarbanes-Oxley, FINRA, EudraLex Annex 11, CJIS, and more. The fine-tuned admin settings, policies, and security tools provide granular data control necessary to meet a wide array of compliance requirements.
FileCloud's data residency options noted above are particularly important for organizations subject to regulations that restrict where data can be stored or processed. The platform's flexible deployment model allows organizations to maintain complete control over data location while still providing modern collaboration capabilities, whether self-hosted or cloud-hosted.
The FileCloud platform also supports unlimited file versioning (for protection against data loss and ransomware), along with custom metadata management and content classification. Advanced features unlock hierarchical retention policies, Smart Data Leak Prevention (DLP), and Smart Content Classification (automated content classification at file upload).
FileCloud admins can boost content classification by integrating with OpenAI, for AI-powered classification rule building. This integration helps streamline rule-building and expands automation capacity across content management to suit rapidly shifting business landscapes.

Dropbox vs FileCloud: Content Management
Beyond basic file storage and sharing, FileCloud offers advanced content management capabilities that position it as more than just a Dropbox alternative. The platform includes version control features that go beyond Dropbox's limited one year retention history.
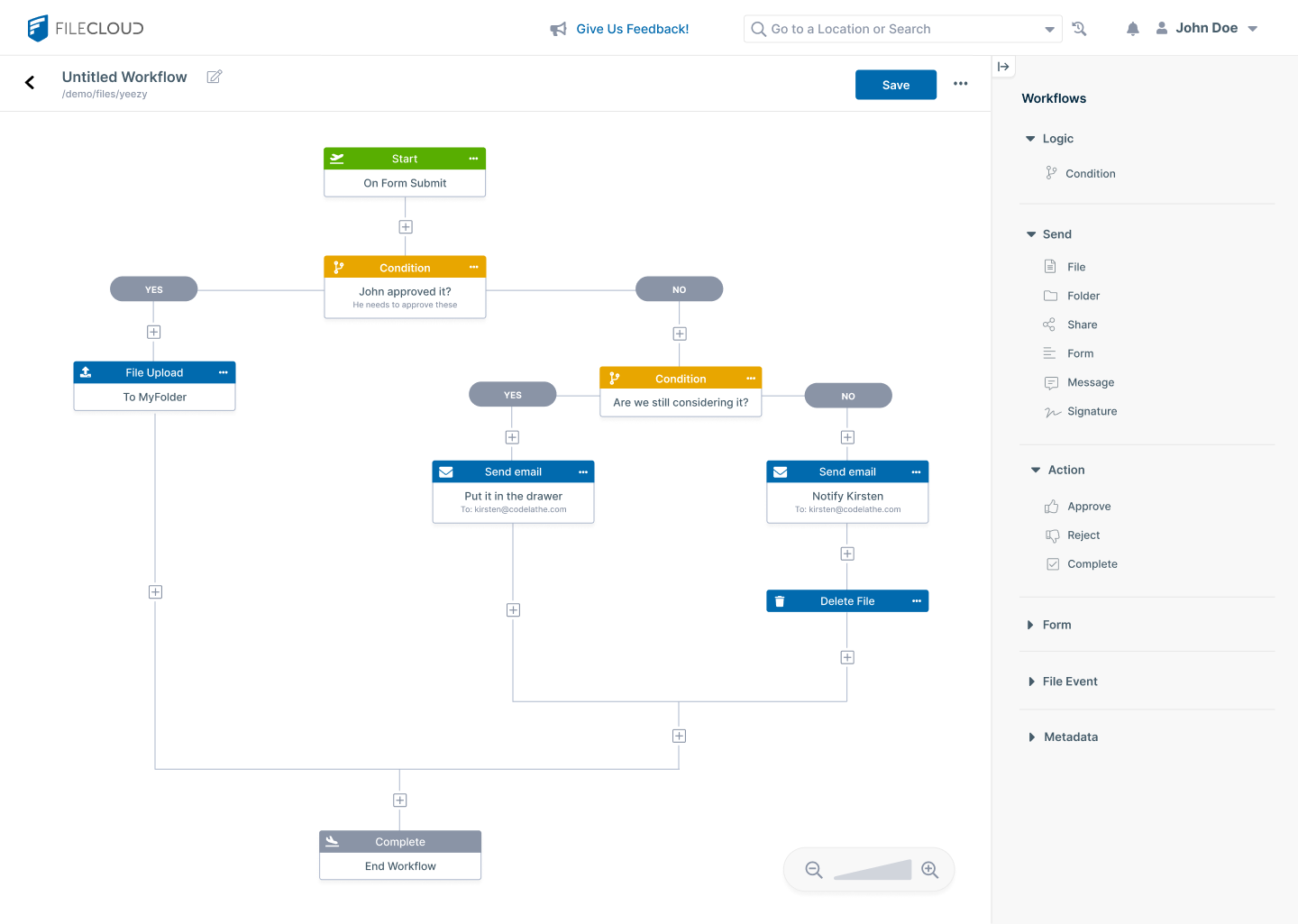
FileCloud's content management features include workflow automation with a drag-and-drop builder that empowers employees to build sophisticated document management systems. The FileCloud platform also supports advanced metadata management, automated file classification, and content lifecycle management features that help organizations maintain organized, searchable file repositories.
Dropbox vs FileCloud: Collaboration & Sharing
Both platforms support file sharing and collaboration, with the ability to set organization-wide policies for external sharing, link expiration, and access permissions. Users can leverage real-time co-authoring capabilities, commenting and annotation tools, and integration with popular productivity suites.
One key difference between FileCloud and Dropbox comes into play with large file sharing. Dropbox supports file sharing for files up to 100 GB. For most situations, this may be functionally enough. However, industries like legal services, finance, media, and engineering often need to coordinate on large files, which requires a secure, streamlined EFSS like FileCloud with granular sharing capabilities.
This large file sharing capability is particularly important for multinational conglomerates and global enterprises that coordinate with partners, contractors, and vendors in mainland China for engineering and manufacturing. The Chinese Firewall blocks many public cloud service providers, including Dropbox. FileCloud is an EFSS solution that enables large file sharing within and beyond Hong Kong and mainland China, thanks to the fine-tuned compliance tools, data residency, and deployment options.
Dropbox vs FileCloud: Remote (Mobile) Access
FileCloud provides comprehensive mobile device management features that give IT administrators control over how corporate data is accessed on personal and corporate devices. Features include mobile device encryption, remote wipe capabilities, and detailed mobile access policies that can restrict functionality based on device compliance status, location, or other factors determined by organizational policies.
The platform supports offline access capabilities that allow users to work with files even when connectivity is limited, with automatic synchronization when connections are restored. This feature is particularly valuable for field workers, traveling employees, and organizations with distributed workforces.
Dropbox vs FileCloud: Conclusion
The choice between FileCloud and Dropbox ultimately comes down to your organization's priorities and requirements. If you're looking for a simple, consumer-friendly file sharing solution with broad market adoption, Dropbox remains a viable option. However, if your organization requires a flexible deployment configuration, robust compliance support, strict data governance controls, and large file sharing capabilities, FileCloud emerges as the superior choice.
As an EFSS Dropbox alternative, FileCloud offers enterprise-focused features without sacrificing usability or functionality. The platform's flexible deployment model, comprehensive security architecture, and advanced administrative capabilities make it particularly well-suited for organizations in regulated industries or those with specific data sovereignty requirements.
Ready to see how FileCloud can address your organization's specific requirements? Sign up for a free trial to experience the platform firsthand, or check out our on-demand demo to see FileCloud's enterprise features in action.

Product Marketing Manager